Table of contents
- Description
- Plugin Name and Description
- Specifying Required Information from the host
PPPDataPPP deploy()Implementation
Tutorial 6 - Call and Response
In this tutorial, we will be using the same model as the previous tutorials, so make sure you have completed the previous tutorials. Also, in this excercise, we will focus on a single thread implementation (as explained in Tutorial 5),
the source code for this tutorial is available in the tutorials branch of the repository.
Description
The objective here is to build a call and response plugin with the following assumptions:
- The user starts playing a sequence of notes
- Once the user stops playing for 2 seconds, we move on to generate a response
- To generate the response:
- we will detect the call section
- Then, we will generate a 4 bar drum pattern based on the call section
- Finally, we will concatenate the generated drum patterns to create the response
- If the user starts playing again, we will stop playback of generations immediately and wait for the user to stop playing again
Plugin Name and Description
As mentioned here, we need to specify the name of the plugin as well as some descriptions for it.
To do this, we will modify the NeuralMidiFXPlugin/NeuralMidiFXPlugin/CMakeLists.txt file as follows:
project(Tutorial6NMFx VERSION 0.0.1)
set (BaseTargetName Tutorial6NMFx)
....
juce_add_plugin("${BaseTargetName}"
COMPANY_NAME "AIMCTutorials"
...
PLUGIN_CODE AZCP # a unique 4 character code for your plugin
...
PRODUCT_NAME "Tutorial6NMFx") # Replace with your plugin title
Once you re-build the cmake project, and re-build the plugin, you should see the name of the plugin change in the DAW:
Now we are ready to move on to the next step.
Specifying Required Information from the host
For specifying what information we need from the DAW, we will be modifying the Configs_HostEvents.h
We need to decide which of the following events are required from the host
| Event Type | Check Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FirstBufferEvent* | new_event_from_host->isFirstBufferEvent() | Sent at the beginning of the host start. |
| PlaybackStoppedEvent* | new_event_from_host->isPlaybackStoppedEvent() | Sent when the host stops the playback. |
| NewBufferEvent | new_event_from_host->isNewBufferEvent() | Sent at the beginning of every new buffer or when qpm, meter, etc. changes. |
| NewBarEvent | new_event_from_host->isNewBarEvent() | Sent at the beginning of every new bar. |
| NewTimeShiftEvent | new_event_from_host->isNewTimeShiftEvent() | Sent every N QuarterNotes (as specified in the configs file |
| NoteOnEvent | new_event_from_host->isNoteOnEvent() | Sent when a note is played. |
| NoteOffEvent | new_event_from_host->isNoteOffEvent() | Sent when a note is stopped. |
| CCEvent | new_event_from_host->isCCEvent() | Sent for Control Change events. |
- -> Always sent by the host
The most obvious one is the NoteOnEvent, which we will need to use for creating the inputs to the model. As such, we should make sure that these event are not filtered out by the wrapper
// Configs_HostEvents.h
namespace event_communication_settings {
// ....
// Filter Note On Events if you don't need them
constexpr bool FilterNoteOnEvents_FLAG{false}; <--- Must be false
}
One more thing to consider here is that we need to keep track of the time since last played note. This is because we need to know when the user has stopped playing for 2 seconds. To do this, we will request the NewBufferEvent from the host. This event is sent as soon as a new buffer is provided to the plugin. This way we will always be able to keep track of time
// Configs_HostEvents.h
namespace event_communication_settings {
// ....
// set to true, if you need to send the metadata for a new buffer to the ITP thread
constexpr bool SendEventAtBeginningOfNewBuffers_FLAG{true}; <--- Must be true
constexpr bool SendEventForNewBufferIfMetadataChanged_FLAG{false}; <--- Must be false (otherwise sent on tempo, meter, etc. changes)
}
whenever the above flag is set, you need to also double check the
SendEventForNewBufferIfMetadataChanged_FLAGflag. This flag is used to specify whether theNewBufferEventshould always be sent or should be sent only when the metadata (tempo, meter, … ) changes.
Lastly, let’s assuming that there is a click track with which the user is synchronizing. To this end, let’s also enabe NewBarEvent events
// ...
constexpr bool SendNewBarEvents_FLAG{true};
// ...
Now we are ready to move on to the next step.
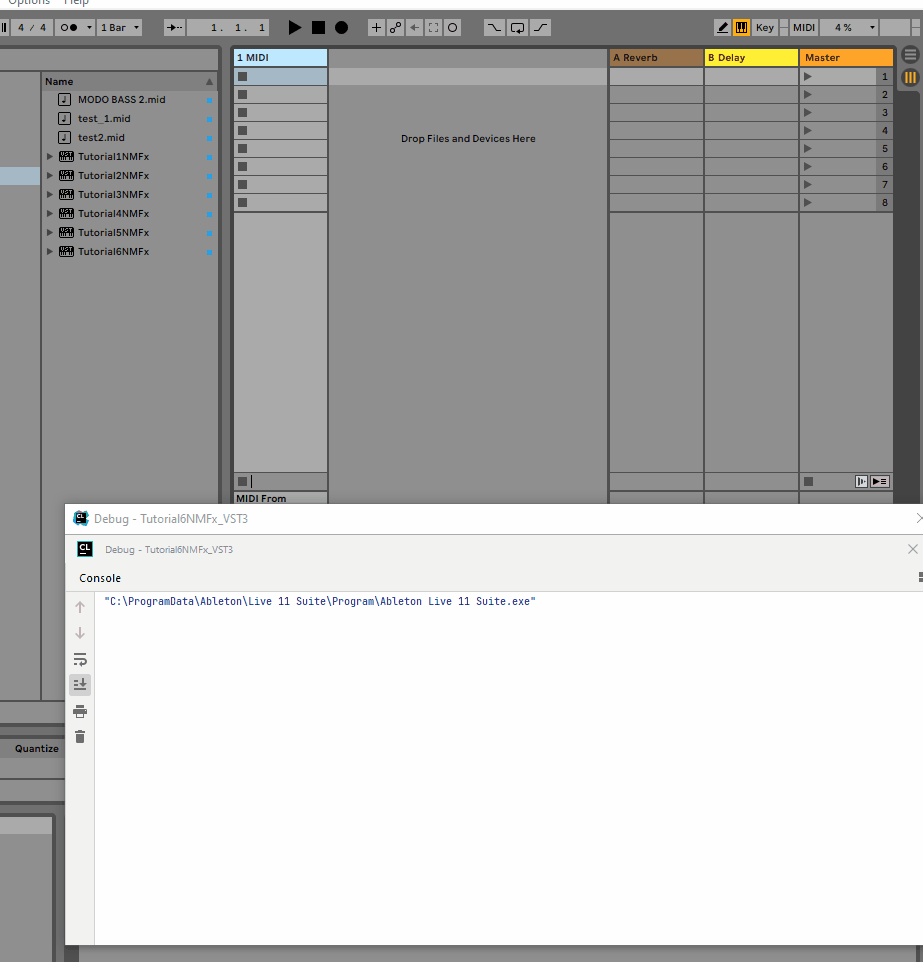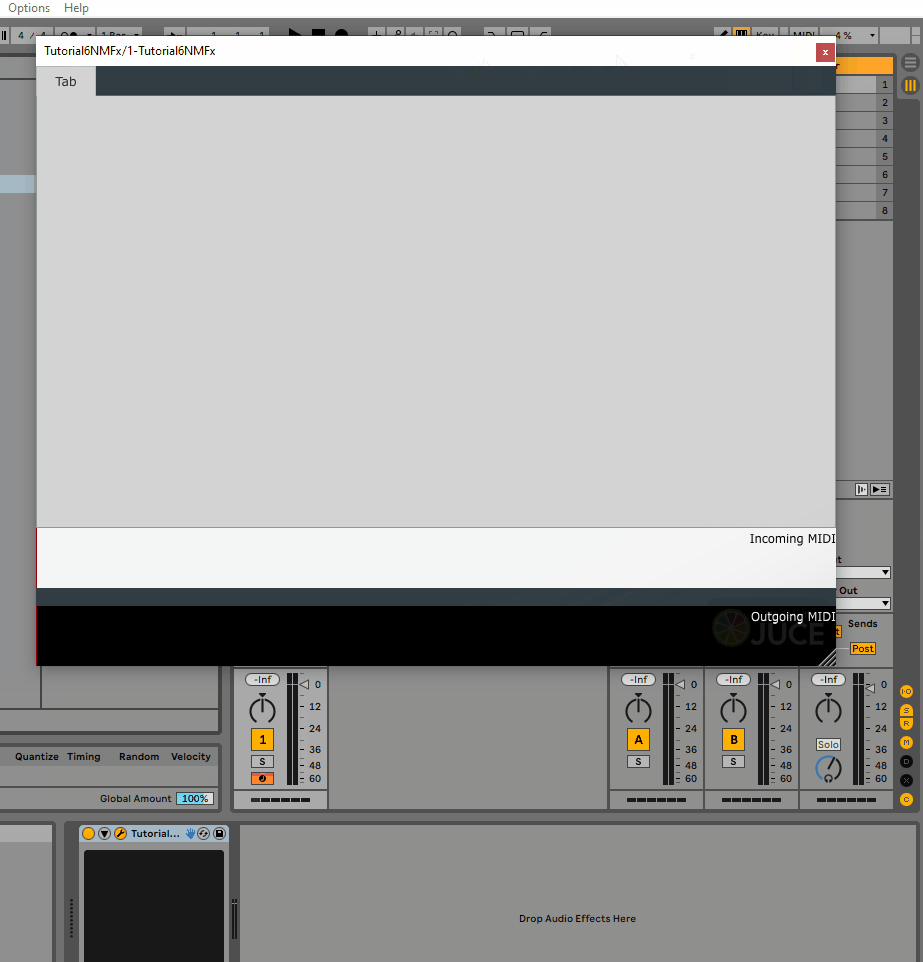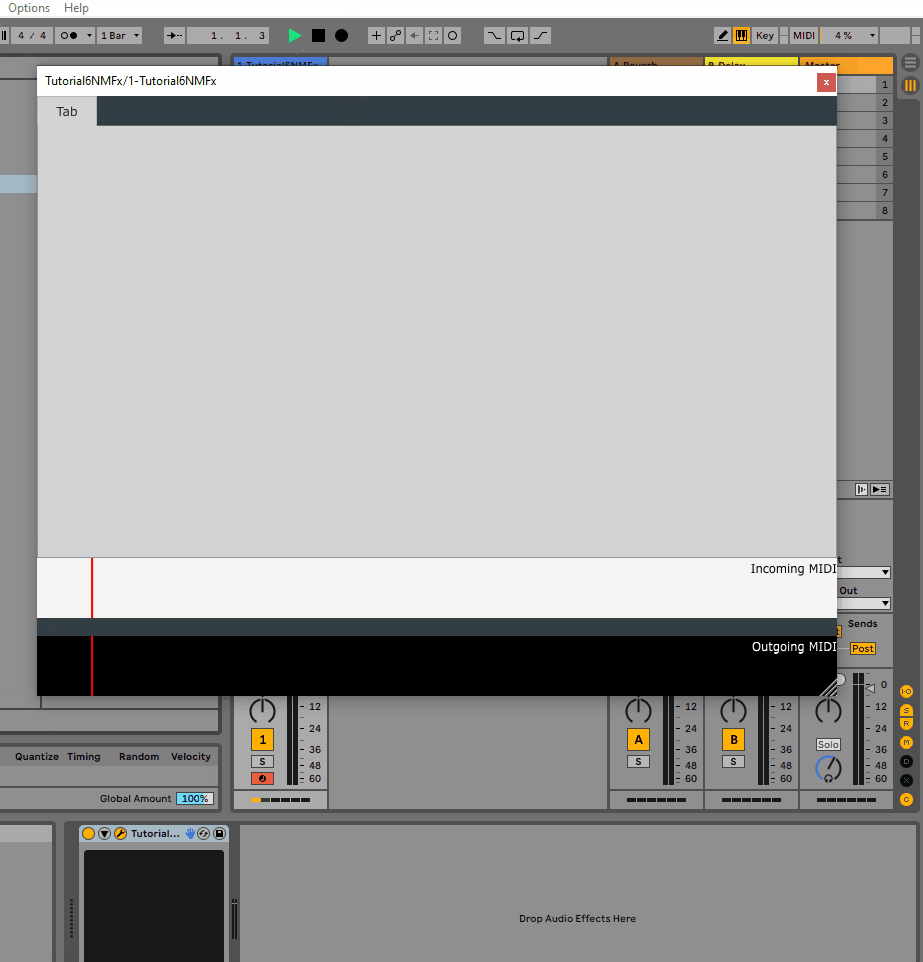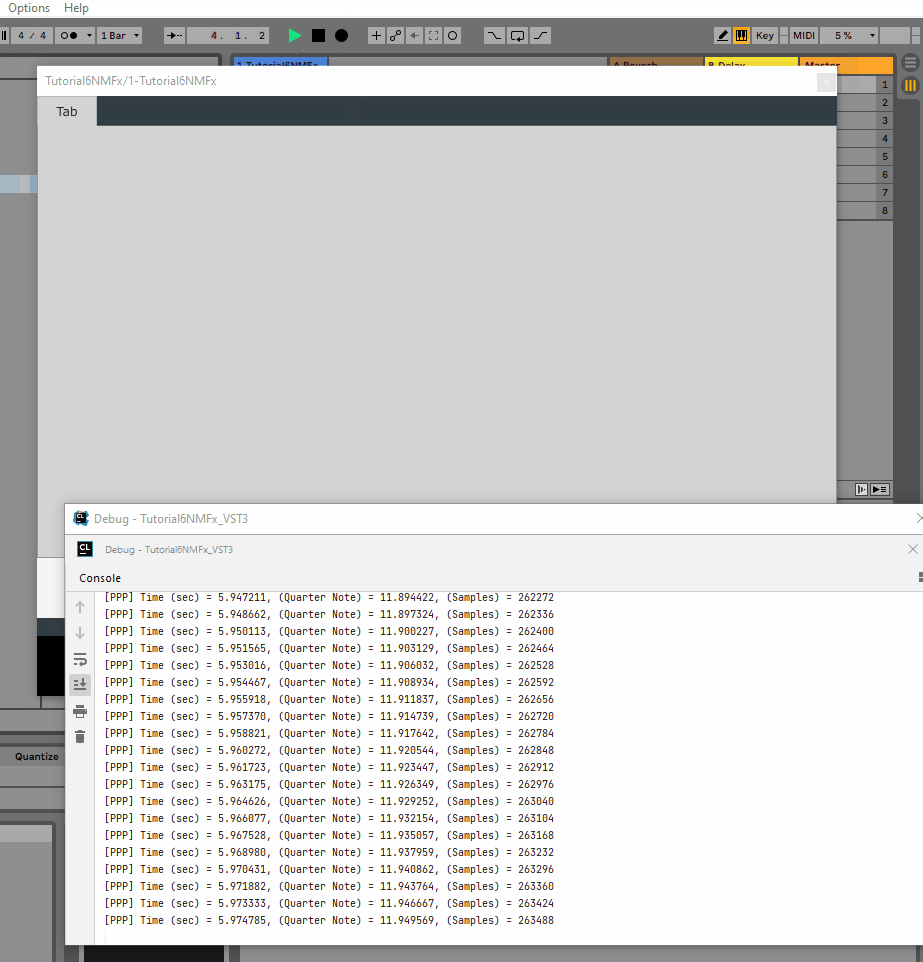
To check that the above settings are correct, let’s print some information to the console.
Given that we are working with a single thread implementation, we will be using the PPP thread only! So to print the information, we will be updating the PPP_Deploy().cpp file.
// PPP_Deploy().cpp
std::pair<bool, bool> PlaybackPreparatorThread::deploy(bool new_model_output_received, bool did_any_gui_params_change) {
bool newPlaybackPolicyShouldBeSent = false;
bool newPlaybackSequenceGeneratedAndShouldBeSent = false;
if (new_model_output_received)
{
// check if any host data is received from model thread via model_output
auto new_event_from_host = model_output.new_event_from_host;
if (new_event_from_host.has_value()) {
if (new_event_from_host->isFirstBufferEvent() ||
new_event_from_host->isPlaybackStoppedEvent() ||
new_event_from_host->isNewBufferEvent()) {
PrintMessage(
"Time (sec) = " +
std::to_string(new_event_from_host->Time().inSeconds()) +
", (Quarter Note) = " +
std::to_string(new_event_from_host->Time().inQuarterNotes()) +
", (Samples) = " +
std::to_string(new_event_from_host->Time().inSamples())
);
}
}
}
return {newPlaybackPolicyShouldBeSent, newPlaybackSequenceGeneratedAndShouldBeSent};
}
We can see that we can correctly access time even if no notes are played.
PPPData
Before we carry on with the implementation of the Deploy function, let’s take a step back and think about the implementation.
Question 1: Do we need to process incoming notes as they arrive?
- This is certainly a possibility, however, for the sake of simplicity, we will process the notes only when it’s time to respond (i.e. 2 seconds after the last note is played)
- So, we will need to have a vector and fill it up with incoming notes so as to process them later
Question 2: How do we detect the start of a call section?
- Because we assumed that the user uses a click track to synchronize with the plugin, we can assume that the call section starts at a bar location
- We can use the
NewBarEventto keep track of the bar locations - Then adjust the timings of notes with respect to these bar locations
As a result, let’s update the PPPData struct in Configs_CustomStructs.h to include the following
// Configs_CustomStructs.h
// Any Extra Variables You need in PPP can be defined here
// An instance called 'PPPdata' will be provided to you in Deploy() method
struct PPPData {
// the scripted model to be used for inference
torch::jit::script::Module model = load_processing_script("drumLoopVAE.pt");
// Bar Locations
std::vector<double> bar_locations;
// Time of the last note played
double last_note_time = 0.0;
// Note On Events Since Call Section Started
std::vector<EventFromHost> note_on_events_since_call_section_started;
// Flag to check if in response section (assume user starts first)
bool UserPerformanceIsBeingRecorded_FLAG = true;
};
Now we are ready to implement the Deploy function.
PPP deploy() Implementation
For this part we’ll be modifying the PPP_Deploy.cpp
Let’s start with keeping track of the user performance
// PPP_Deploy().cpp
std::pair<bool, bool> PlaybackPreparatorThread::deploy(bool new_model_output_received, bool did_any_gui_params_change) {
bool newPlaybackPolicyShouldBeSent = false;
bool newPlaybackSequenceGeneratedAndShouldBeSent = false;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Call Section (i.e. user is playing)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
if (new_model_output_received)
{
// check if any host data is received from model thread via model_output
auto new_event_from_host = model_output.new_event_from_host;
if (new_event_from_host.has_value()) {
// store the bar locations
if (new_event_from_host->isNewBarEvent()) {
PPPdata.bar_locations.emplace_back(new_event_from_host->Time().inQuarterNotes());
}
// keep track of played notes
if (new_event_from_host->isNoteOnEvent()) {
// if user is playing. we are in Call section
PPPdata.UserPerformanceIsBeingRecorded_FLAG = true;
// Clear playing generations if any
playbackSequence.clear();
newPlaybackSequenceGeneratedAndShouldBeSent = true;
// store note
PPPdata.note_on_events_since_call_section_started.emplace_back(*new_event_from_host);
// store time of last note
PPPdata.last_note_time = new_event_from_host->Time().inSeconds();
}
// check if two seconds elapsed since last note
if (new_event_from_host->Time().inSeconds() - PPPdata.last_note_time > 2.0) {
// if user is not playing. we are in Response section
// however check if any notes were played, otherwise keep waiting
if (!PPPdata.note_on_events_since_call_section_started.empty()) {
PPPdata.UserPerformanceIsBeingRecorded_FLAG = false;
}
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Response Section (i.e. user is not playing)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// check if we should respond to the user
if (!PPPdata.UserPerformanceIsBeingRecorded_FLAG) {
// Test Code
// -----------------------------------------------------
PrintMessage("Time to generate a new sequence");
PPPdata.note_on_events_since_call_section_started.clear();
PPPdata.UserPerformanceIsBeingRecorded_FLAG = true;
// -----------------------------------------------------
}
}
return {newPlaybackPolicyShouldBeSent, newPlaybackSequenceGeneratedAndShouldBeSent};
}
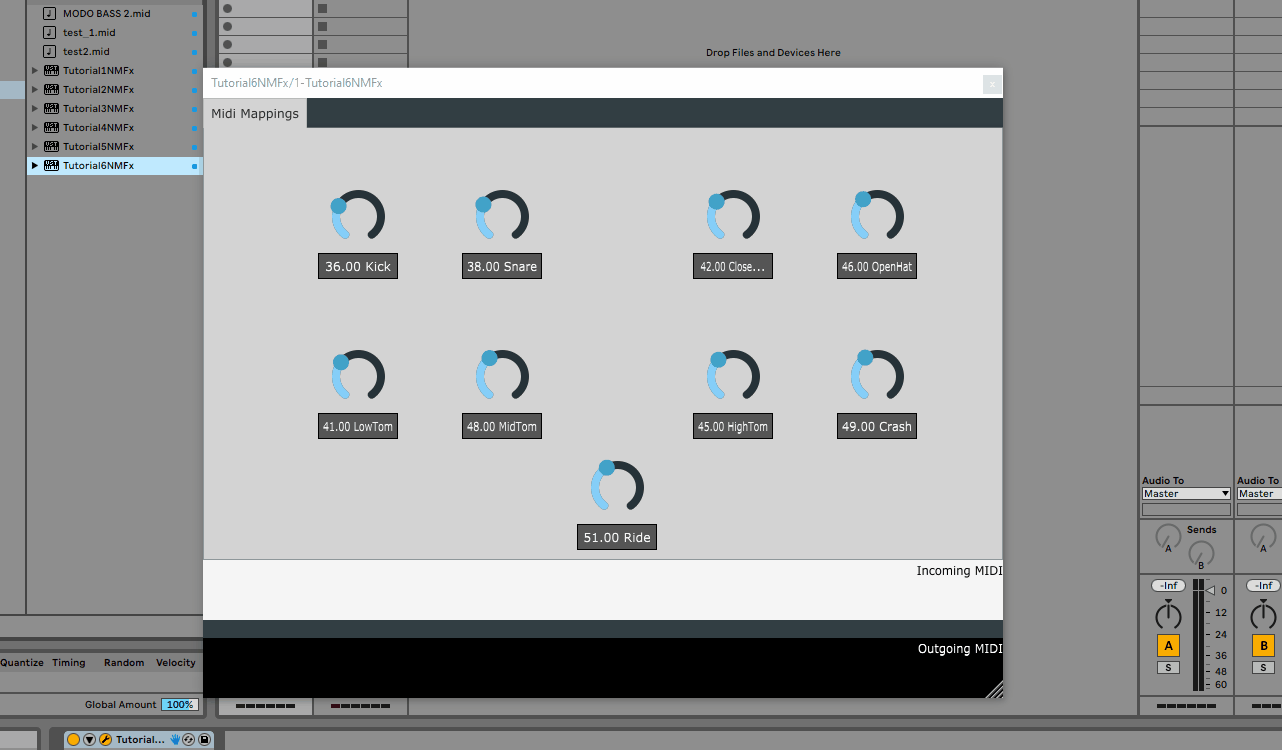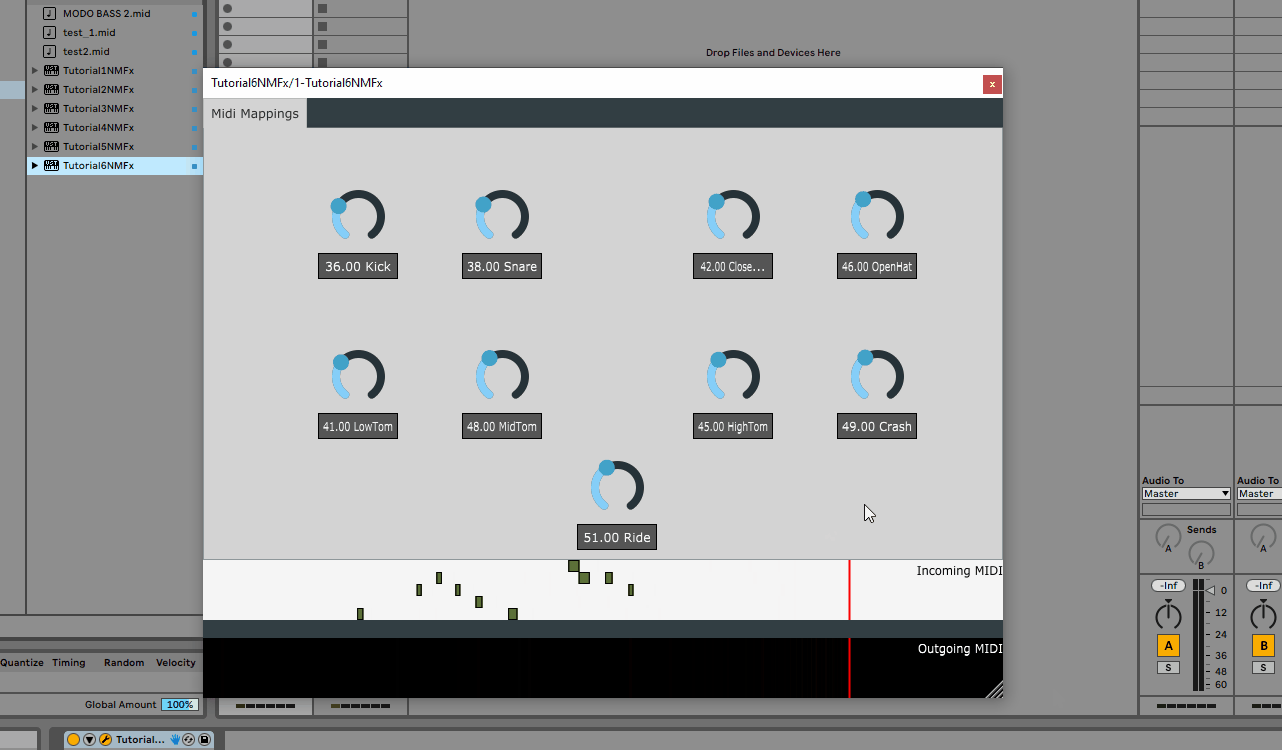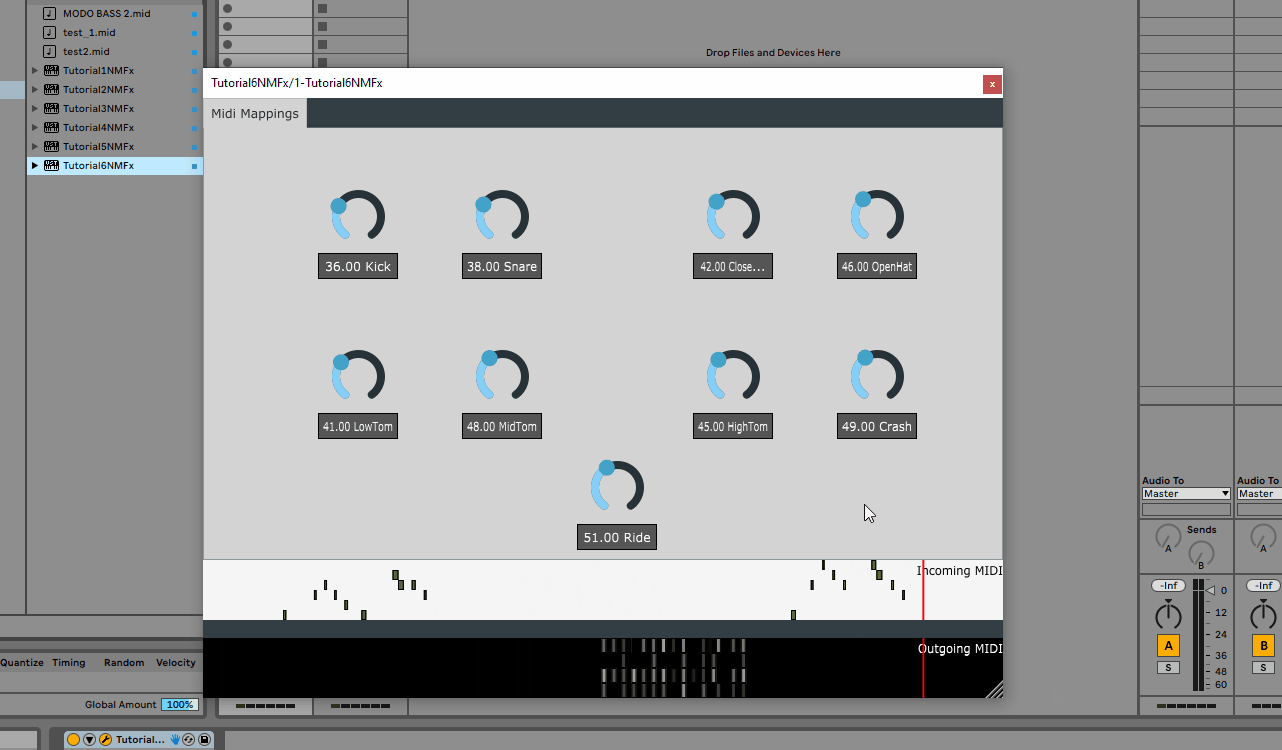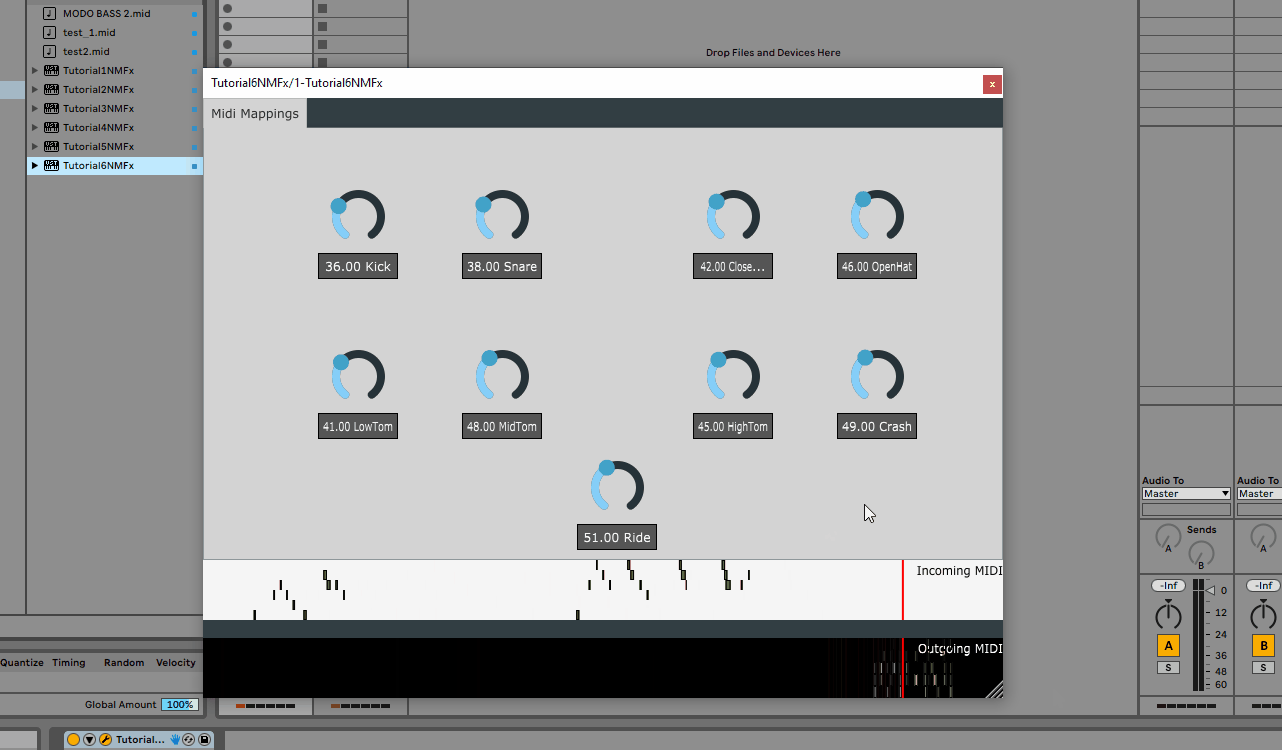
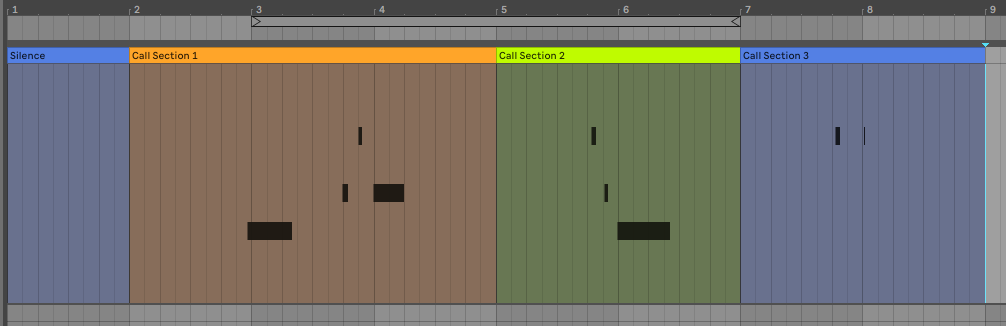
Looking at the input we can see that the detection of call response sections is working as expected. (4 means 1 bar, 16 means 4 bars and 24 means 6 bars; these match the locations in DAW view)
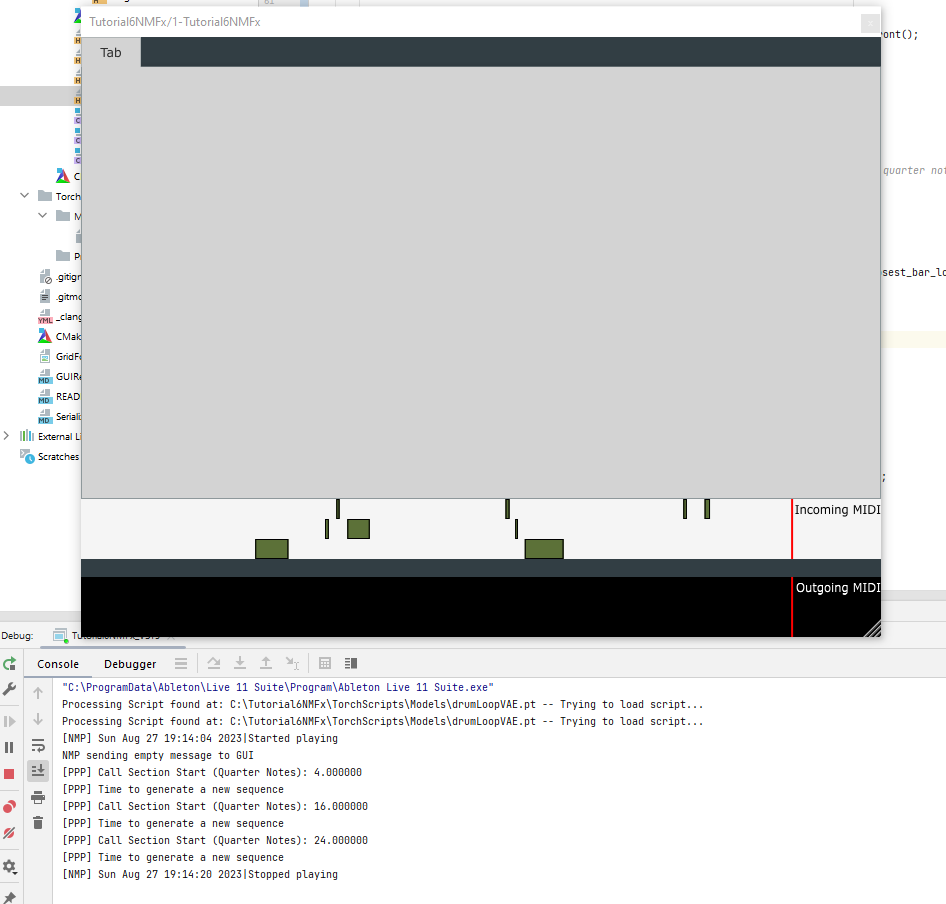
Now that we have the starting location of the call section, we can re-do the previous operations for inference (tutorials 1-4).
I will skip the details here, however, I want to mention one note about the playback policy.
In the previous tutorials, we played the generations in a loop mode. However, here we want to play it once and starting at a bar location. As a result, I use RealtimePlaybackInfo to find the location of an upcoming bar and then adjust the timing of the notes accordingly
// PPP_Deploy().cpp
// ....
// get Upcoming bar location
// find closest higher multiple of 8 to time_now
auto time_now = realtimePlaybackInfo->get().time_in_ppq;
auto upcoming_bar_location = ceil(time_now / 4.0) * 4.0;
// ....
auto time = (step_ix + offset) * 0.25f + upcoming_bar_location;